Lab 1:
Part A:
Prelab + Setup
The Prelab and Step 1 consisted of installing the Arduino IDE and following through the preliminary setup instructions to install and calibrate all the necessary components.
Lab Tasks
Step 2 was used to test whether the Artemis board was connected properly. To accomplish this, I ran the Example Blink. This caused the LED on the Artemis board to blink on and off which ensured that it was properly connected.
Step 3 consisted of following Example4_Serial. This example allowed me to type in a character input and then in turn recieve those same characters as an output in the Serial monitor.
Step 4 tested the temperature sensor using the Example2_analogRead. As you can see below, pressing on the sensor, effectively warming it up, causes the temperature in the Serial monitor to slowly increase.
I then tested the Artemis board’s built in microphone using Example1_MicrophoneOutput. I spoke into the microphone with varying decibels of loudness to see if the microphone would in turn fluctuate at the corresponding frequency.
Part B:
Prelab + Setup
The Prelab and initial steps of this lab consisted of familiarizing myself with BLE, setiting up the virtual environment, and installing the appropriate python packages. Additionally, I modified the UUID and MAC addresses to connect the Artemis board to my laptop.
I used the Artemis address c0:81:a4:22:20:64 and the UUID e81d1925-217b-46e1-8718-ba10e53245d7. To check that the Bluetooth connection was properly established I ran through demo.py and was successful in going through all the code blocks.
Lab Tasks
1. Echo
The first task was to send a string from the computer to the Artemis and then have it return an augmented verson of the string back to the computer such that it prints out “Robot Says -> __ :)” . Following the logic used in the PING case, I was able to adapt my code to accomplish the task.
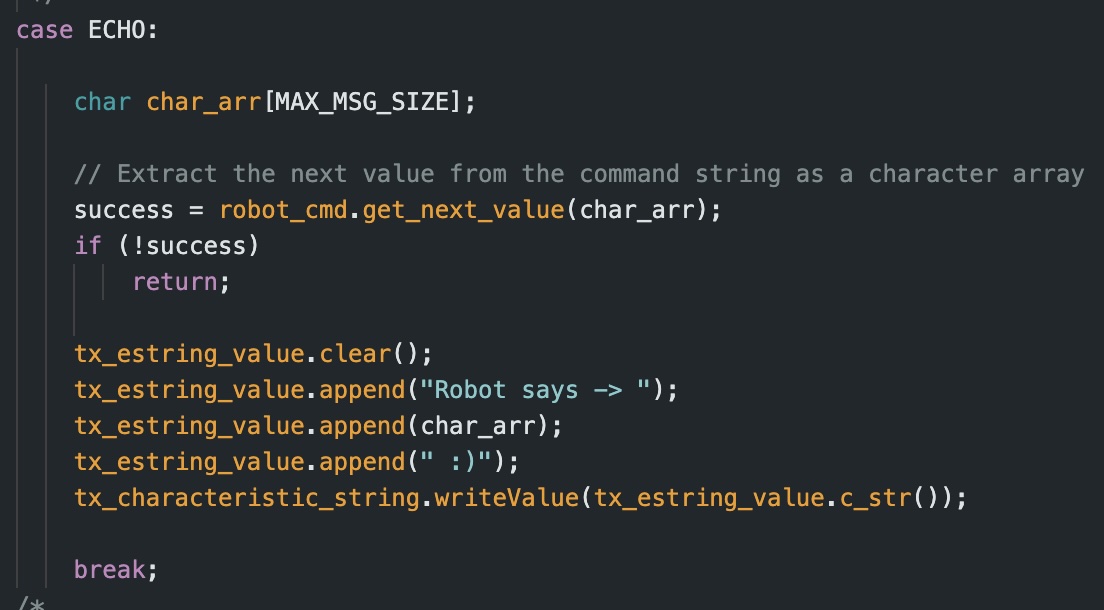
The resulting output from inputting the string “Hello World” can be seen below:

2. Send Three Floats
The second task consisted of writing a command SEND_THREE_FLOATS which sends three floats to the Artemis board and extracts those three values in the Serial monitor. I accomplished this using similar logic to the SEND_TWO_INTS command, adjusting the code to account for three float values instead of int values.
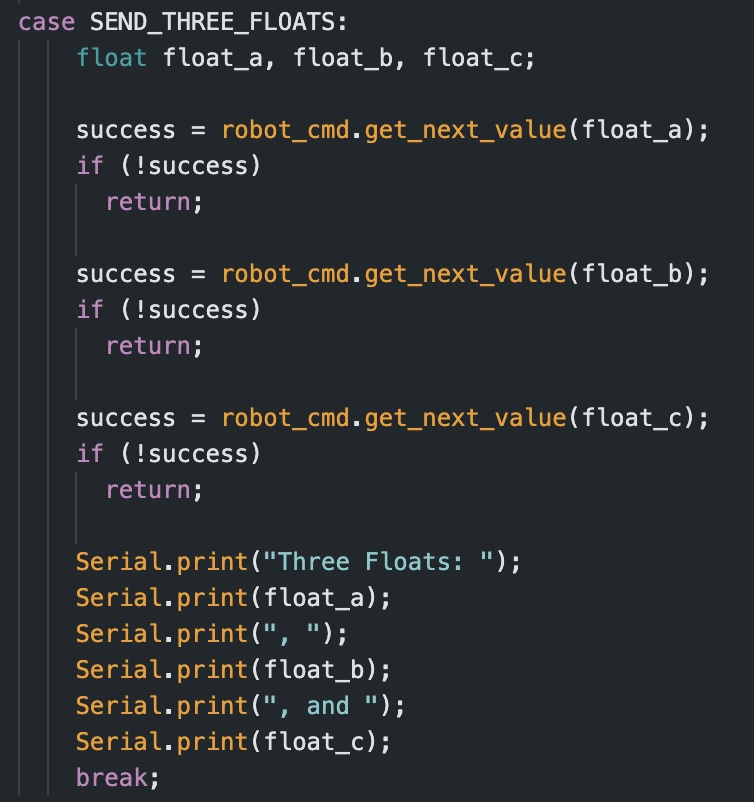
The resulting output from inputting the series of floats 1.1, 2.2, and 3.3 can be seen below:


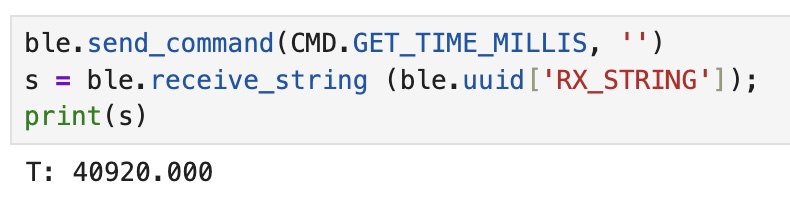
3. Get Time Millis
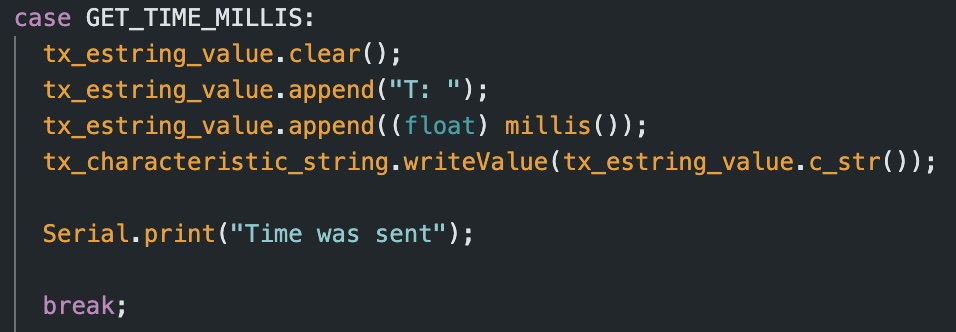
The third task consiste of adding a new command GET_TIME_MILLIS which makes the arduino write a string of the form T:123456 to the string characteristic. To accomplish this, I wrote the following code using the millis() function in Arduino.
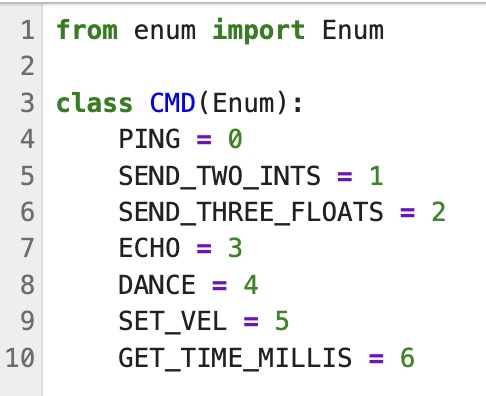
Additionally, I had to add the command to the list found in cmd_types.py.
You can see me successfully calling the funciton in the python code cell below:
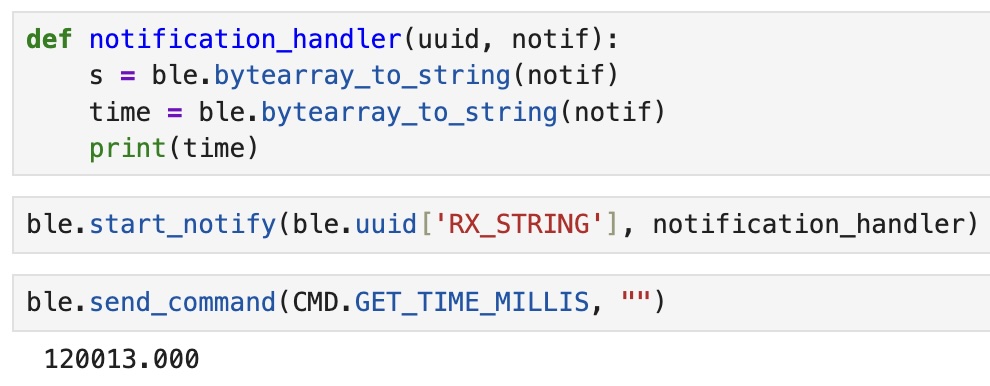
4. Notification Handler
Task four asked us to setup a notification handler to recieve the string value from the Artemis board and extraxt the time from the string. I accomplished this using the following code:
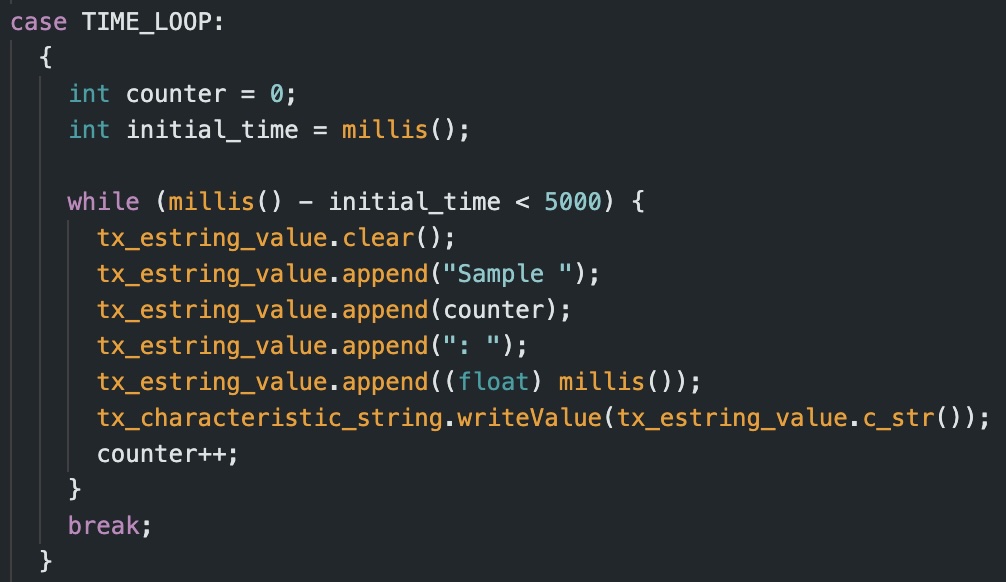
5. Data Transfer Rate
Task five asked us to write a loop that gets the current time and send it to my laptop to be processed by the notification handler set up in step 4. Using the following arduino code, I collected values for approximately 5 seconds.
I found that in 5 seconds my code was able to collect time data samples 203 times.
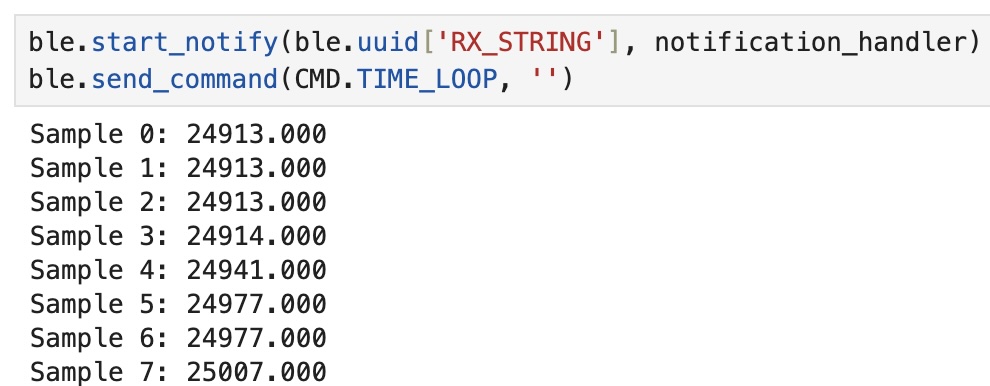

From this I was able to calculate that the effective data transfer rate is 203/5 or approximately 40.6 messages per second.
6. Send Time Data
7. Get Temperature Readings
8. Data Transfer Rate Discussion
Dicussion
Through my completion of this lab, I was able to develop a deeper understanding of different python concepts which I wasn’t exposed to before. For Lab 1, given my lack of expereince, I relied on former student pages as a helpful resource for trouble shooting my problems. Particularly, I referenced Nila’s page as well as TA Daria’s page. They were very helpful in exposing me to new functions which I was able to adapt, in turn advancing my own understanding of Python and its application as it pertains to this course. Additionally, the Python classes link on the course website was particulalry helpful.